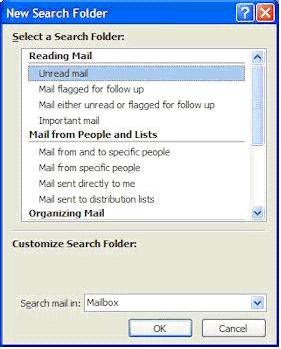
In the Mail Folders list, navigate to the Search Folders option under your Mailbox
Search this Blog
Saturday, August 22, 2009
Dealing With Disappearing “Unread Mail” Folder In Outlook 2007
In the Mail Folders list, navigate to the Search Folders option under your Mailbox
Wednesday, August 19, 2009
Exe’s not opening. Showing the option Open with
You might be facing some issue that the exe’s will not open directly and it will show an option to open with. This is because of the corrupted registry. Copy the below thing in notepad and save it with the extension .reg and added the entry into registry.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.exe]
@="exefile"
"Content Type"="application/x-msdownload"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.exe\PersistentHandler]
@="{098f2470-bae0-11cd-b579-08002b30bfeb}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile]
@="Application"
"EditFlags"=hex:38,07,00,00
"TileInfo"="prop:FileDescription;Company;FileVersion"
"InfoTip"="prop:FileDescription;Company;FileVersion;Create;Size"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\DefaultIcon]
@="%1"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shell]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shell\open]
"EditFlags"=hex:00,00,00,00
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shell\open\command]
@="\"%1\" %*"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shell\runas]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shell\runas\command]
@="\"%1\" %*"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shellex]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shellex\DropHandler]
@="{86C86720-42A0-1069-A2E8-08002B30309D}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shellex\PropertySheetHandlers]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shellex\PropertySheetHandlers\PEAnalyser]
@="{09A63660-16F9-11d0-B1DF-004F56001CA7}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shellex\PropertySheetHandlers\PifProps]
@="{86F19A00-42A0-1069-A2E9-08002B30309D}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shellex\PropertySheetHandlers\ShimLayer Property Page]
@="{513D916F-2A8E-4F51-AEAB-0CBC76FB1AF8}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\regfile]
@="Registration Entries"
"EditFlags"=dword:00100000
"BrowserFlags"=dword:00000008
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\regfile\DefaultIcon]
@=hex(2):25,00,53,00,79,00,73,00,74,00,65,00,6d,00,52,00,6f,00,6f,00,74,00,25,\
00,5c,00,72,00,65,00,67,00,65,00,64,00,69,00,74,00,2e,00,65,00,78,00,65,00,\
2c,00,31,00,00,00
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\regfile\shell]
@="open"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\regfile\shell\edit]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\regfile\shell\edit\command]
@=hex(2):25,00,53,00,79,00,73,00,74,00,65,00,6d,00,52,00,6f,00,6f,00,74,00,25,\
00,5c,00,73,00,79,00,73,00,74,00,65,00,6d,00,33,00,32,00,5c,00,4e,00,4f,00,\
54,00,45,00,50,00,41,00,44,00,2e,00,45,00,58,00,45,00,20,00,25,00,31,00,00,\
00
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\regfile\shell\open]
@="Mer&ge"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\regfile\shell\open\command]
@="regedit.exe \"%1\""
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\regfile\shell\print]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\regfile\shell\print\command]
@=hex(2):25,00,53,00,79,00,73,00,74,00,65,00,6d,00,52,00,6f,00,6f,00,74,00,25,\
00,5c,00,73,00,79,00,73,00,74,00,65,00,6d,00,33,00,32,00,5c,00,4e,00,4f,00,\
54,00,45,00,50,00,41,00,44,00,2e,00,45,00,58,00,45,00,20,00,2f,00,70,00,20,\
00,25,00,31,00,00,00
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.lnk]
@="lnkfile"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.lnk\ShellEx]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.lnk\ShellEx\{000214EE-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}]
@="{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.lnk\ShellEx\{000214F9-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}]
@="{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.lnk\ShellEx\{00021500-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}]
@="{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.lnk\ShellEx\{BB2E617C-0920-11d1-9A0B-00C04FC2D6C1}]
@="{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.lnk\ShellNew]
"Command"="rundll32.exe appwiz.cpl,NewLinkHere %1"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\lnkfile]
@="Shortcut"
"EditFlags"=dword:00000001
"IsShortcut"=""
"NeverShowExt"=""
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\lnkfile\CLSID]
@="{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\lnkfile\shellex]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\lnkfile\shellex\ContextMenuHandlers]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\lnkfile\shellex\ContextMenuHandlers\Offline Files]
@="{750fdf0e-2a26-11d1-a3ea-080036587f03}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\lnkfile\shellex\ContextMenuHandlers\{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\lnkfile\shellex\DropHandler]
@="{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\lnkfile\shellex\IconHandler]
@="{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\lnkfile\shellex\PropertySheetHandlers]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\lnkfile\shellex\PropertySheetHandlers\ShimLayer Property Page]
@="{513D916F-2A8E-4F51-AEAB-0CBC76FB1AF8}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}]
@="Shortcut"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}\InProcServer32]
@="shell32.dll"
"ThreadingModel"="Apartment"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}\PersistentAddinsRegistered]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}\PersistentAddinsRegistered\{89BCB740-6119-101A-BCB7-00DD010655AF}]
@="{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}\PersistentHandler]
@="{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}\ProgID]
@="lnkfile"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}\shellex]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}\shellex\MayChangeDefaultMenu]
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Repair/Reset Winsock settings
Most of the Internet connectivity problems arise out of corrupt Winsock settings. Windows sockets settings may get corrupted due to the installation of a networking software, or perhaps due to Malware infestation. You will be able connect to the Internet, but the packets won't transfer back and forth. And errors such as Page cannot be displayed may occur when using Internet Explorer.
Windows XP Service Pack 2 - New Winsock NETSH commands
Two new Netsh commands are available in Windows XP Service Pack 2.
netsh winsock reset catalog
This command resets the Winsock catalog to the default configuration. This can be useful if a malformed LSP is installed that results in loss of network connectivity. While use of this command can restore network connectivity, it should be used with care because any previously-installed LSPs will need to be re-installed.
netsh winsock show catalog
This command displays the list of Winsock LSPs that are installed on the computer.
To output the results to a file type this in Command Prompt (CMD.EXE)
netsh winsock show catalog >C:\lsp.txt
Use a manual method to reset TCP/IP
Reset command is available in the IP context of the NetShell utility. Follow these steps to use the reset command to reset TCP/IP manually:
To open a command prompt, click Start and then click Run. Copy and paste (or type) the following command in the Open box and then press ENTER:
cmd
At the command prompt, copy and paste (or type) the following command and then press ENTER:
netsh int ip reset c:\resetlog.txt
Note If you do not want to specify a directory path for the log file, use the following command:
netsh int ip reset resetlog.txt
Reboot the computer.
When you run the reset command, it rewrites two registry keys that are used by TCP/IP. This has the same result as removing and reinstalling the protocol. The reset command rewrites the following two registry keys:
SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters\
SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\DHCP\Parameters\
To run the manual command successfully, you must specify a file name for the log, in which the actions that netsh takes will be recorded. When you run the manual command, TCP/IP is reset and the actions that were taken are recorded in the log file, known as resetlog.txt in this article. The first example, c:\resetlog.txt, creates a path where the log will reside. The second example, resetlog.txt, creates the log file in the current directory. In either case, if the specified log file already exists, the new log will be appended to the end of the existing file.
Registry Entry for Enabling Hidden Files & Folders
1. Click “Start” -> “Run…” (or press Windows key + R)
2. Type “regedit” and click “Ok”.
3. Find the key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced\Folder\Hidden\SHOWALL
4. Look at the “CheckedValue” key… This should be a DWORD key. If it isn’t, delete the key.
5. Create a new key called “CheckedValue” as a DWORD (hexadecimal) with a value of 1.
6. The “Show hidden files & folders” check box should now work normally.
Or
Copy the below and save it as .reg extn in notepad and run it.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced\Folder\Hidden\NOHIDDEN]
"RegPath"="Software\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Explorer\\Advanced"
"Text"="@shell32.dll,-30501"
"Type"="radio"
"CheckedValue"=dword:00000002
"ValueName"="Hidden"
"DefaultValue"=dword:00000002
"HKeyRoot"=dword:80000001
"HelpID"="shell.hlp#51104"
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced\Folder\Hidden\SHOWALL]
"RegPath"="Software\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Explorer\\Advanced"
"Text"="@shell32.dll,-30500"
"Type"="radio"
"CheckedValue"=dword:00000001
"ValueName"="Hidden"
"DefaultValue"=dword:00000002
"HKeyRoot"=dword:80000001
"HelpID"="shell.hlp#51105"
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
To remove protectfile.vbs virus from the system
1. Download the free tool MoveOnBoot
2. Open MoveOnBoot
3. Go to Rename Action -> Rename File
4. A dialog box will open, select the file. Since these virus files are hidden files , you won’t be able to browse and see it. Please enter enter “C:\protectfile.vbs” in select-file section.
5. Enter “C:\protectfile.html” in the destination file section. Enter OK.
6. Similarly repeat steps 2 to 4 for the file “C:\autorun.inf” and rename it to “C:\autorun.html”
7. Don’t restart your computer. We have set moveonboot to rename the ProtectFile.vbs in just one of the drives.
8. Repeat step 2 to 5 for each of the drives. For example if you have 4 drives in your computer(C, D, E, F), then you will have to rename “C:\protectfile.vbs”, “D:\protectfile.vbs”, “E:\protectfile.vbs” and “F:\protectfile.vbs” to “C:\protectfile.html”, “D:\protectfile.html”, “E:\protectfile.html” and “F:\protectfile.html” respectively. Similarly rename “autorun.inf” files in all the drives to corresponding “autorun.html” files.
9. Restart your computer. We have disabled the virus.
10. Now we will remove them completely.
11. Open MoveOnBoot again.
12. Go to Delete Actions -> Delete Files
13. You won’t be able to browse and reach the files. So click browse and enter “C:\protectfile.html”, “D:\protectfile.html”, “E:\protectfile.html” ,”F:\protectfile.html”, “C:\autorun.html”, “D:\autorun.html”, “E:\autorun.html” and “F:\autorun.html”
14. Restart your computer.
To remove protectfile.vbs from your system
1. Go to Task manager(Press Ctrl+Alt+Del).
2. In the Processes tab , Kill the processes : explorer and wscript.exe(if available)
3. Now go to Applications tab and press new task
4. Enter cmd .Go to the drive c:\
5. Type del /f/q/a protectfile.vbsand del /f/q/a autorun.inf
6. Go to c:\windows\system32and enter del /f/q/a secureguard.vbsNow you have deleted all the infected files in your system
7. Goto regedit(enter regedit in Run) and search for protectfile.vbs and delete all entries with this name.
8. Now search for the secureguard.vbs and modify it as in the path del only"c:\windows\system32\secureguard.vbs... and let the other part of the path be there alive..
9. Restart your system
Configure TCP/IP from the Command Prompt
In order to configure TCP/IP settings such as the IP address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, DNS and WINS addresses and many other options you can use Netsh.exe.
Netsh.exe is a command-line scripting utility that allows you to, either locally or remotely, display or modify the network configuration of a computer that is currently running. Netsh.exe also provides a scripting feature that allows you to run a group of commands in batch mode against a specified computer. Netsh.exe can also save a configuration script in a text file for archival purposes or to help you configure other servers.
Netsh.exe is available on Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003.
You can use the Netsh.exe tool to perform the following tasks:
Configure interfaces
Configure routing protocols
Configure filters
Configure routes
Configure remote access behavior for Windows-based remote access routers that are running the Routing and Remote Access Server (RRAS) Service
Display the configuration of a currently running router on any computer
Use the scripting feature to run a collection of commands in batch mode against a specified router.
What can we do with Netsh.exe?
With Netsh.exe you can easily view your TCP/IP settings. Type the following command in a Command Prompt window (CMD.EXE):
netsh interface ip show config
With Netsh.exe, you can easily configure your computer's IP address and other
TCP/IP related settings. For example:
The following command configures the interface named Local Area Connection with the static IP address 192.168.0.100, the subnet mask of 255.255.255.0, and a default gateway of 192.168.0.1:
netsh interface ip set address name="Local Area Connection" static 192.168.0.100 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.1 1
(The above line is one long line, copy paste it as one line)
Netsh.exe can be also useful in certain scenarios such as when you have a portable computer that needs to be relocated between 2 or more office locations, while still maintaining a specific and static IP address configuration. With Netsh.exe, you can easily save and restore the appropriate network configuration.
First, connect your portable computer to location #1, and then manually configure the required settings (such as the IP address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, DNS and WINS addresses).
Now, you need to export your current IP settings to a text file. Use the following command:
netsh -c interface dump > c:'location1.txt
When you reach location #2, do the same thing, only keep the new settings to a different file:
netsh -c interface dump > c:'location2.txt
You can go on with any other location you may need, but we'll keep it simple and only use 2 examples.
Now, whenever you need to quickly import your IP settings and change them between location #1 and location #2, just enter the following command in a Command Prompt window (CMD.EXE):
netsh -f c:'location1.txt
or
netsh -f c:'location2.txt
and so on.
You can also use the global EXEC switch instead of -F:
netsh exec c:'location2.txt
Netsh.exe can also be used to configure your NIC to automatically obtain an IP address from a DHCP server:
netsh interface ip set address "Local Area Connection" dhcp
Would you like to configure DNS and WINS addresses from the Command Prompt? You can. See this example for DNS:
netsh interface ip set dns "Local Area Connection" static 192.168.0.200
and this one for WINS:
netsh interface ip set wins "Local Area Connection" static 192.168.0.200
Or, if you want, you can configure your NIC to dynamically obtain it's DNS settings:
netsh interface ip set dns "Local Area Connection" dhcp
As you now see, Netsh.exe has many features you might find useful, and that goes beyond saying even without looking into the other valuable options that exist in the command