Link for the script:- AD-Management-Tasks
Search this Blog
Monday, April 09, 2018
Script to perform day to day Active Directory Tasks
Link for the script:- AD-Management-Tasks
Tuesday, December 22, 2015
Exchange PowerShell Commands
[PS] C:\Users\sysadmin\Desktop>Get-Mailbox -Identity "Nagarajan S" | For
mat-List Name,Database,UseDatabaseQuotaDefaults,IssueWarningQuota,ProhibitSendRe
ceiveQuota,MaxSendSize,MaxReceiveSize,RecipientLimits,PrimarySmtpAddress,Organiz
ationalUnit,RecipientType,ServerName
Command to get Mail Forwarding Enabled Users
Get-Mailbox -Filter {ForwardingAddress -ne $null} | ft Name,ForwardingAddress,DeliverToMailboxAndForward -Autosize
Forefront Powershell command to get blocked email of a user
PS C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Forefront Protection for Exchange Server>Get-FseQuarantine | Where-Object {$_.RecipientAddresses -eq "s.nagarajan@testdomain.com"} | Select-object -property "SenderName","SenderAddress","Subject","DetectionTime","IncidentCategory","IncidentName","RecipientNames"
To get the mailbox size of the users in an OU
get-mailbox -OrganizationalUnit "ou=IT,ou=Users,dc=testdomain,dc=net" -resultsize unlimited | get-mailboxstatistics | ft DisplayName,TotalItemSize,Itemcount
Setting mail enabled security group to restrict mail delivery to DL
Set-DistributionGroup Test-ChennaiDL -AcceptMessagesOnlyFromDLMembers "ALL_MAIL SENDERS"
Sunday, June 03, 2012
Step by Step Configuring SAN storage in Windows 2003 Server using MS iSCSI Initiator
Monday, May 28, 2012
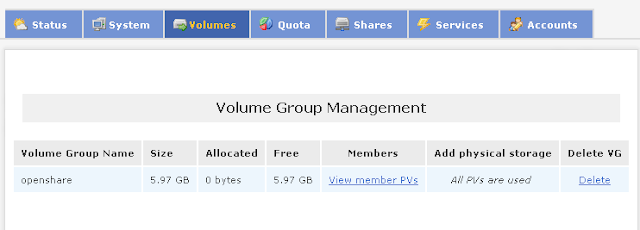
Step by Step Configuring Openfiler Storage
Here i will show how you can setup a SAN storage using Openfiler to use with VMware Workstation.
- Install Openfiler as a separate VM.
- Once successfully installed the Openfiler you will get the screen below.
4. Before this ensure the httpd service and openfiler service is running, if not start those services by running the following commands.
19. Now go to the Volumes tab and select ‘Network ACL’.Here we can found the storage which we created in the previous step. Select ‘Allow’ from the access drop down list and click Update button as this will allow the iSCSI Target to be accessed by the host or the subnet which we setup earlier.

Monday, June 27, 2011
Windows 2003 Interview Questions-2
How do you double-boot a Win 2003 server box? The Boot.ini file is set as read-only, system, and hidden to prevent unwanted editing. To change the Boot.ini timeout and default settings, use the System option in Control Panel from the Advanced tab and select Startup.
What do you do if earlier application doesn’t run on Windows Server 2003? When an application that ran on an earlier legacy version of Windows cannot be loaded during the setup function or if it later malfunctions, you must run the compatibility mode function. This is accomplished by right-clicking the application or setup program and selecting Properties –> Compatibility –> selecting the previously supported operating system.
If you uninstall Windows Server 2003, which operating systems can you revert to? Win ME, Win 98, 2000, XP. Note, however, that you cannot upgrade from ME and 98 to Windows Server 2003.
How do you get to Internet Firewall settings? Start –> Control Panel –> Network and Internet Connections –> Network Connections.
What are the Windows Server 2003 keyboard shortcuts? Winkey opens or closes the Start menu. Winkey + BREAK displays the System Properties dialog box. Winkey + TAB moves the focus to the next application in the taskbar. Winkey + SHIFT + TAB moves the focus to the previous application in the taskbar. Winkey + B moves the focus to the notification area. Winkey + D shows the desktop. Winkey + E opens Windows Explorer showing My Computer. Winkey + F opens the Search panel. Winkey + CTRL + F opens the Search panel with Search for Computers module selected. Winkey + F1 opens Help. Winkey + M minimizes all. Winkey + SHIFT+ M undoes minimization. Winkey + R opens Run dialog. Winkey + U opens the Utility Manager. Winkey + L locks the computer.
What is Active Directory? Active Directory is a network-based object store and service that locates and manages resources, and makes these resources available to authorized users and groups. An underlying principle of the Active Directory is that everything is considered an object—people, servers, workstations, printers, documents, and devices. Each object has certain attributes and its own security access control list (ACL).
Where are the Windows NT Primary Domain Controller (PDC) and its Backup Domain Controller (BDC) in Server 2003? The Active Directory replaces them. Now all domain controllers share a multimaster peer-to-peer read and write relationship that hosts copies of the Active Directory.
How long does it take for security changes to be replicated among the domain controllers? Security-related modifications are replicated within a site immediately. These changes include account and individual user lockout policies, changes to password policies, changes to computer account passwords,
and modifications to the Local Security Authority (LSA).
What’s new in Windows Server 2003 regarding the DNS management? When DC promotion occurs with an existing forest, the Active Directory Installation Wizard contacts an existing DC to update the directory and replicate from the DC the required portions of the directory. If the wizard fails to locate a DC, it performs debugging and reports what caused the failure and how to fix the problem. In order to be located on a network, every DC must register in DNS DC locator DNS records. The Active Directory Installation Wizard verifies a proper configuration of the DNS infrastructure. All DNS configuration debugging and reporting activity is done with the Active Directory Installation Wizard.
When should you create a forest? Organizations that operate on radically different bases may require separate trees with distinct namespaces. Unique trade or brand names often give rise to separate DNS identities. Organizations merge or are acquired and naming continuity is desired. Organizations form
partnerships and joint ventures. While access to common resources is desired, a separately defined tree can enforce more direct administrative and security restrictions.
How can you authenticate between forests? Four types of authentication are used across forests: (1) Kerberos and NTLM network logon for remote access to a server in another forest; (2) Kerberos and NTLM interactive logon for physical logon outside the user‘s home forest; (3) Kerberos delegation to N-tier application in another forest; and (4) user principal name (UPN) credentials.
What snap-in administrative tools are available for Active Directory? Active Directory Domains and Trusts Manager, Active Directory Sites and Services Manager, Active Directory Users and Group Manager, Active Directory Replication (optional, available from the Resource Kit), Active Directory Schema Manager (optional, available from adminpak)
What types of classes exist in Windows Server 2003 Active Directory?
Structural class. The structural class is important to the system administrator in that it is the only type from which new Active Directory objects are created. Structural classes are developed from either the
modification of an existing structural type or the use of one or more abstract classes.
Abstract class. Abstract classes are so named because they take the form of templates that actually create other templates (abstracts) and structural and auxiliary classes. Think of abstract classes as frameworks for the defining objects.
Auxiliary class. The auxiliary class is a list of attributes. Rather than apply numerous attributes when creating a structural class, it provides a streamlined alternative by applying a combination of attributes with a single include action.
88 class. The 88 class includes object classes defined prior to 1993, when the 1988 X.500 specification was adopted. This type does not use the structural, abstract, and auxiliary definitions, nor is it in common use for the development of objects in Windows Server 2003 environments.
How do you delete a lingering object? Windows Server 2003 provides a command called Repadmin that provides the ability to delete lingering objects in the Active Directory.
What is Global Catalog? The Global Catalog authenticates network user logons and fields inquiries about objects across a forest or tree. Every domain has at least one GC that is hosted on a domain controller. In Windows 2000, there was typically one GC on every site in order to prevent user logon failures
across the network.
How is user account security established in Windows Server 2003? When an account is created, it is given a unique access number known as a security identifier (SID). Every group to which the user belongs has an associated SID. The user and related group SIDs together form the user account‘s security token, which determines access levels to objects throughout the system and network. SIDs from the security token are mapped to the access control list (ACL) of any object the user attempts to access.
If I delete a user and then create a new account with the same username and password, would the SID and permissions stay the same? No. If you delete a user account and attempt to recreate it with the same user name and password, the SID will be different.
What do you do with secure sign-ons in an organization with many roaming users? Credential Management feature of Windows Server 2003 provides a consistent single sign-on experience for users. This can be useful for roaming users who move between computer systems. The Credential Management feature provides a secure store of user credentials that includes passwords and X.509 certificates.
Anything special you should do when adding a user that has a Mac? "Save password as encrypted clear text" must be selected on User Properties Account Tab Options, since the Macs only store their passwords that way.
What remote access options does Windows Server 2003 support? Dial-in, VPN, dial-in with callback.
Where are the documents and settings for the roaming profile stored? All the documents and environmental settings for the roaming user are stored locally on the system, and, when the user logs off, all changes to the locally stored profile are copied to the shared server folder. Therefore, the first time a roaming user logs on to a new system the logon process may take some time, depending on how large his profile folder is.
Where are the settings for all the users stored on a given machine? \Document and Settings\All Users
What languages can you use for log-on scripts? JavaScipt, VBScript, DOS batch files (.com, .bat, or even .exe)
Friday, June 24, 2011
Windows 2003 Interview Questions-1
What’s the difference between local, global and universal groups? Domain local groups assign access permissions to global domain groups for local domain resources. Global groups provide access to resources in other trusted domains. Universal groups grant access to resources in all trusted domains.
I am trying to create a new universal user group. Why can’t I? Universal groups are allowed only in native-mode Windows Server 2003 environments. Native mode requires that all domain controllers be promoted to Windows Server 2003 Active Directory.
What is LSDOU? It‘s group policy inheritance model, where the policies are applied to Local machines, Sites, Domains and Organizational Units.
Why doesn’t LSDOU work under Windows NT? If the NTConfig.pol file exist, it has the highest priority among the numerous policies.
Where are group policies stored? %SystemRoot%System32\GroupPolicy
What is GPT and GPC? Group policy template and group policy container.
Where is GPT stored? %SystemRoot%\SYSVOL\sysvol\domainname\Policies\GUID
You change the group policies, and now the computer and user settings are in conflict. Which one has the highest priority? The computer settings take priority.
You want to set up remote installation procedure, but do not want the user to gain access over it. What do you do? gponame–> User Configuration–> Windows Settings–> Remote Installation Services–> Choice Options is your friend.
What’s contained in administrative template conf.adm? Microsoft NetMeeting policies
How can you restrict running certain applications on a machine? Via group policy, security settings for the group, then Software Restriction Policies.
You need to automatically install an app, but MSI file is not available. What do you do? A .zap text file can be used to add applications using the Software Installer, rather than the Windows Installer.
What’s the difference between Software Installer and Windows Installer? The former has fewer privileges and will probably require user intervention. Plus, it uses .zap files.
What can be restricted on Windows Server 2003 that wasn’t there in previous products? Group Policy in Windows Server 2003 determines a users right to modify network and dial-up TCP/IP properties. Users may be selectively restricted from modifying their IP address and other network
configuration parameters.
How frequently is the client policy refreshed? 90 minutes give or take.
Where is secedit? It‘s now gpupdate.
You want to create a new group policy but do not wish to inherit.? Make sure you check Block inheritance among the options when creating the policy.
What is "tattooing" the Registry? The user can view and modify user preferences that are not stored in maintained portions of the Registry. If the group policy is removed or changed, the user preference will persist in the Registry.
How do you fight tattooing in NT/2000 installations? You can‘t.
How do you fight tattooing in 2003 installations? User Configuration - Administrative Templates - System - Group Policy - enable - Enforce Show Policies Only.
What does IntelliMirror do? It helps to reconcile desktop settings, applications, and stored files for users, particularly those who move between workstations or those who must periodically work offline.
What’s the major difference between FAT and NTFS on a local machine? FAT and FAT32 provide no security over locally logged-on users. Only native NTFS provides extensive permission control on both remote and local files.
How do FAT and NTFS differ in approach to user shares? They don‘t, both have support for sharing.
Explan the List Folder Contents permission on the folder in NTFS.?Same as Read & Execute, but not inherited by files within a folder. However, newly created subfolders will inherit this permission.
I have a file to which the user has access, but he has no folder permission to read it. Can he access it? It is possible for a user to navigate to a file for which he does not have folder permission. This involves simply knowing the path of the file object. Even if the user can‘t drill down the
file/folder tree using My Computer, he can still gain access to the file using the Universal Naming Convention (UNC). The best way to start would be to type the full path of a file into Run… window.
For a user in several groups, are Allow permissions restrictive or permissive? Permissive, if at least one group has Allow permission for the file/folder, user will have the same permission.
For a user in several groups, are Deny permissions restrictive or permissive? Restrictive, if at least one group has Deny permission for the file/folder, user will be denied access, regardless of other group permissions.
What hidden shares exist on Windows Server 2003 installation? Admin$, Drive$, IPC$, NETLOGON, print$ and SYSVOL.
What’s the difference between standalone and fault-tolerant DFS (Distributed File System) installations? The standalone server stores the Dfs directory tree structure or topology locally. Thus, if a shared folder is inaccessible or if the Dfs root server is down, users are left with no link to the
shared resources. A fault-tolerant root node stores the Dfs topology in the Active Directory, which is replicated to other domain controllers. Thus, redundant root nodes may include multiple connections to the same data residing in different shared folders.
We’re using the DFS fault-tolerant installation, but cannot access it from a Win98 box. Use the UNC path, not client, only 2000 and 2003 clients can access Server 2003 fault-tolerant shares.
Where exactly do fault-tolerant DFS shares store information in Active Directory? In Partition Knowledge Table, which is then replicated to other domain controllers.
Can you use Start->Search with DFS shares? Yes.
What problems can you have with DFS installed? Two users opening the redundant copies of the file at the same time, with no file-locking involved in DFS, changing the contents and then saving. Only one file will be propagated through DFS.
I run Microsoft Cluster Server and cannot install fault-tolerant DFS. Yeah, you can‘t. Install a standalone one.
Is Kerberos encryption symmetric or asymmetric? Symmetric.
How does Windows 2003 Server try to prevent a middle-man attack on encrypted line? Time stamp is attached to the initial client request, encrypted with the shared key.
What hashing algorithms are used in Windows 2003 Server? RSA Data Security‘s Message Digest 5 (MD5), produces a 128-bit hash, and the Secure Hash Algorithm 1 (SHA-1), produces a 160-bit hash.
What third-party certificate exchange protocols are used by Windows 2003 Server? Windows Server 2003 uses the industry standard PKCS-10 certificate request and PKCS-7 certificate response to exchange CA certificates with third-party certificate authorities.
What’s the number of permitted unsuccessful logons on Administrator account? Unlimited. Remember, though, that it‘s the Administrator account, not any account that‘s part of the Administrators group.
If hashing is one-way function and Windows Server uses hashing for storing passwords, how is it possible to attack the password lists, specifically the ones using NTLMv1? A cracker would launch a dictionary attack by hashing every imaginable term used for password and then compare the hashes.
What’s the difference between guest accounts in Server 2003 and other editions? More restrictive in Windows Server 2003.
How many passwords by default are remembered when you check "Enforce Password History Remembered"? User‘s last 6 passwords.
Thursday, December 24, 2009
Restore Show Desktop Icon to Quick Launch on Taskbar
Open Notepad and enter the following text:
[Shell]
Command=2
IconFile=explorer.exe,3
[Taskbar]
Command=ToggleDesktop
Save the new file as Show Desktop.scf then drag and drop the icon on the Quick Launch bar or whatever location you want the shortcut to appear.
Using the Regsvr32 command
Click Start, Run and type the following command:
regsvr32 /n /i:U shell32.dll
The Show Desktop icon file should be available now.
Thursday, September 17, 2009
Outlook Search Not working
1) Open the Outlook search option panel and unselect all folders for indexing.
2) Exit Outlook and without doing anything else wait a good while,(I waited 15 minutes) it was suggested that you allow time for the index to be removed.
3) Reboot
4) Go directly to the control panel, go to System and Maintenence, then to Indexing Options, then to Advanced Options.
5) Press the Reset Defaults button (yes if you have special options you will loose them)
6) Reboot and wait for the indexes to rebuild (this may take quite a long time).
7) When you return to Outlook you will see the Indexing Status now actually works its way through the items and when it completes the Instant search works.
Tuesday, September 01, 2009
How to Remove the Background Color of the Desktop Icons

- Right click on the desktop and hover on “Arrange Icons By”.- From the appeared sub-menu, select “Lock Web Items on Desktop”.- If it is checked, “uncheck” it.
- Right click on the desktop and select “Properties”.- “Display Properties” window appears. Click on the “Desktop” tab.- Click on the “Customize Desktop” button.- On the “Desktop Items” you can add/remove or modify desktop items. Check “Lock desktop items” from the “Web” tab.
- Right click on “My Computer” and select “Properties”.- Choose the “Advanced” tab, then click on the “Setting” button.- You can check or uncheck the settings to the ones preferred.
If you are not sure of the appropriate settings, you may choose “Let Windows choose what’s best for my computer” or “Adjust for best appearance” as well.
Renaming Recycle Bin
1. Click Start
3. Type regedit and hit ENTER
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\ShellNoRoam\MUICache
5. Double click on the following value:@C:\WINDOWS\system32\SHELL32.dll,-8964
7. Click OK and close out regedit
9. After the screen refreshes, you recycle bin will be renamed to whatever you decided
Open up your favorite plain text editor (notepad, for example) and copy the
following text into a new file:
REGEDIT4
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{645FF040-5081-101B-9F08-00AA002F954E}\ShellFolder]"Attributes"=hex:50,01,00,20
"CallForAttributes"=dword:00000000
Now save this text file as a .reg file, such as "Rename Recycle Bin.reg" and
put it wherever you like. Double click on the file, and when it asks you if
you want to import it into the registry, choose Yes. You'll notice a new
option in the right-click menu to Rename the Recycle Bin. You can also
rename it by highlighing the Bin and hitting F2, or by highlighting it and
clicking on the file name (just like renaming any other file.
If you want to turn off this new feature, make another .reg file with the
same content as above, but change the first number in the "Attributes"=hex:
line from 50 to 40 and import that file into the registry.
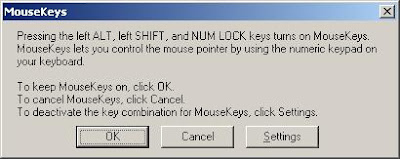
How to move your mouse cursor without mouse?
Follow the given steps to activate the keyboard mouse:
To edit this feature, first you should log onto your computer with administrative rights.
To activate this feature, press Alt+Shift+NumLock keys at once and you will receive a small MouseKey box.
Click on Settings button, if you want to adjust the mouse cursor detail settings.
Now using Numeric keypad, you can move your mouse pointer. The controls are:
· 1,2,3,4,6,7,8 and 9 keys are used to move the mouse cursor into different directions.
· Key 5 is used as mouse click button.
· Insert key used to hold down mouse button.
· + Sign used to double click on any object.
· Delete button used to release the mouse. Click on NumLock button to disable this keyboard mouse feature
Saturday, August 22, 2009
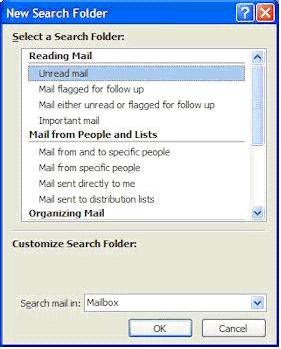
Dealing With Disappearing “Unread Mail” Folder In Outlook 2007
In the Mail Folders list, navigate to the Search Folders option under your Mailbox
Wednesday, August 19, 2009
Exe’s not opening. Showing the option Open with
You might be facing some issue that the exe’s will not open directly and it will show an option to open with. This is because of the corrupted registry. Copy the below thing in notepad and save it with the extension .reg and added the entry into registry.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.exe]
@="exefile"
"Content Type"="application/x-msdownload"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.exe\PersistentHandler]
@="{098f2470-bae0-11cd-b579-08002b30bfeb}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile]
@="Application"
"EditFlags"=hex:38,07,00,00
"TileInfo"="prop:FileDescription;Company;FileVersion"
"InfoTip"="prop:FileDescription;Company;FileVersion;Create;Size"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\DefaultIcon]
@="%1"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shell]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shell\open]
"EditFlags"=hex:00,00,00,00
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shell\open\command]
@="\"%1\" %*"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shell\runas]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shell\runas\command]
@="\"%1\" %*"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shellex]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shellex\DropHandler]
@="{86C86720-42A0-1069-A2E8-08002B30309D}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shellex\PropertySheetHandlers]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shellex\PropertySheetHandlers\PEAnalyser]
@="{09A63660-16F9-11d0-B1DF-004F56001CA7}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shellex\PropertySheetHandlers\PifProps]
@="{86F19A00-42A0-1069-A2E9-08002B30309D}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\exefile\shellex\PropertySheetHandlers\ShimLayer Property Page]
@="{513D916F-2A8E-4F51-AEAB-0CBC76FB1AF8}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\regfile]
@="Registration Entries"
"EditFlags"=dword:00100000
"BrowserFlags"=dword:00000008
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\regfile\DefaultIcon]
@=hex(2):25,00,53,00,79,00,73,00,74,00,65,00,6d,00,52,00,6f,00,6f,00,74,00,25,\
00,5c,00,72,00,65,00,67,00,65,00,64,00,69,00,74,00,2e,00,65,00,78,00,65,00,\
2c,00,31,00,00,00
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\regfile\shell]
@="open"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\regfile\shell\edit]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\regfile\shell\edit\command]
@=hex(2):25,00,53,00,79,00,73,00,74,00,65,00,6d,00,52,00,6f,00,6f,00,74,00,25,\
00,5c,00,73,00,79,00,73,00,74,00,65,00,6d,00,33,00,32,00,5c,00,4e,00,4f,00,\
54,00,45,00,50,00,41,00,44,00,2e,00,45,00,58,00,45,00,20,00,25,00,31,00,00,\
00
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\regfile\shell\open]
@="Mer&ge"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\regfile\shell\open\command]
@="regedit.exe \"%1\""
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\regfile\shell\print]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\regfile\shell\print\command]
@=hex(2):25,00,53,00,79,00,73,00,74,00,65,00,6d,00,52,00,6f,00,6f,00,74,00,25,\
00,5c,00,73,00,79,00,73,00,74,00,65,00,6d,00,33,00,32,00,5c,00,4e,00,4f,00,\
54,00,45,00,50,00,41,00,44,00,2e,00,45,00,58,00,45,00,20,00,2f,00,70,00,20,\
00,25,00,31,00,00,00
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.lnk]
@="lnkfile"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.lnk\ShellEx]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.lnk\ShellEx\{000214EE-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}]
@="{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.lnk\ShellEx\{000214F9-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}]
@="{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.lnk\ShellEx\{00021500-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}]
@="{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.lnk\ShellEx\{BB2E617C-0920-11d1-9A0B-00C04FC2D6C1}]
@="{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\.lnk\ShellNew]
"Command"="rundll32.exe appwiz.cpl,NewLinkHere %1"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\lnkfile]
@="Shortcut"
"EditFlags"=dword:00000001
"IsShortcut"=""
"NeverShowExt"=""
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\lnkfile\CLSID]
@="{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\lnkfile\shellex]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\lnkfile\shellex\ContextMenuHandlers]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\lnkfile\shellex\ContextMenuHandlers\Offline Files]
@="{750fdf0e-2a26-11d1-a3ea-080036587f03}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\lnkfile\shellex\ContextMenuHandlers\{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\lnkfile\shellex\DropHandler]
@="{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\lnkfile\shellex\IconHandler]
@="{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\lnkfile\shellex\PropertySheetHandlers]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\lnkfile\shellex\PropertySheetHandlers\ShimLayer Property Page]
@="{513D916F-2A8E-4F51-AEAB-0CBC76FB1AF8}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}]
@="Shortcut"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}\InProcServer32]
@="shell32.dll"
"ThreadingModel"="Apartment"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}\PersistentAddinsRegistered]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}\PersistentAddinsRegistered\{89BCB740-6119-101A-BCB7-00DD010655AF}]
@="{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}\PersistentHandler]
@="{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}\ProgID]
@="lnkfile"
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}\shellex]
[HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{00021401-0000-0000-C000-000000000046}\shellex\MayChangeDefaultMenu]
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Repair/Reset Winsock settings
Most of the Internet connectivity problems arise out of corrupt Winsock settings. Windows sockets settings may get corrupted due to the installation of a networking software, or perhaps due to Malware infestation. You will be able connect to the Internet, but the packets won't transfer back and forth. And errors such as Page cannot be displayed may occur when using Internet Explorer.
Windows XP Service Pack 2 - New Winsock NETSH commands
Two new Netsh commands are available in Windows XP Service Pack 2.
netsh winsock reset catalog
This command resets the Winsock catalog to the default configuration. This can be useful if a malformed LSP is installed that results in loss of network connectivity. While use of this command can restore network connectivity, it should be used with care because any previously-installed LSPs will need to be re-installed.
netsh winsock show catalog
This command displays the list of Winsock LSPs that are installed on the computer.
To output the results to a file type this in Command Prompt (CMD.EXE)
netsh winsock show catalog >C:\lsp.txt
Use a manual method to reset TCP/IP
Reset command is available in the IP context of the NetShell utility. Follow these steps to use the reset command to reset TCP/IP manually:
To open a command prompt, click Start and then click Run. Copy and paste (or type) the following command in the Open box and then press ENTER:
cmd
At the command prompt, copy and paste (or type) the following command and then press ENTER:
netsh int ip reset c:\resetlog.txt
Note If you do not want to specify a directory path for the log file, use the following command:
netsh int ip reset resetlog.txt
Reboot the computer.
When you run the reset command, it rewrites two registry keys that are used by TCP/IP. This has the same result as removing and reinstalling the protocol. The reset command rewrites the following two registry keys:
SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters\
SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\DHCP\Parameters\
To run the manual command successfully, you must specify a file name for the log, in which the actions that netsh takes will be recorded. When you run the manual command, TCP/IP is reset and the actions that were taken are recorded in the log file, known as resetlog.txt in this article. The first example, c:\resetlog.txt, creates a path where the log will reside. The second example, resetlog.txt, creates the log file in the current directory. In either case, if the specified log file already exists, the new log will be appended to the end of the existing file.
Registry Entry for Enabling Hidden Files & Folders
1. Click “Start” -> “Run…” (or press Windows key + R)
2. Type “regedit” and click “Ok”.
3. Find the key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced\Folder\Hidden\SHOWALL
4. Look at the “CheckedValue” key… This should be a DWORD key. If it isn’t, delete the key.
5. Create a new key called “CheckedValue” as a DWORD (hexadecimal) with a value of 1.
6. The “Show hidden files & folders” check box should now work normally.
Or
Copy the below and save it as .reg extn in notepad and run it.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced\Folder\Hidden\NOHIDDEN]
"RegPath"="Software\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Explorer\\Advanced"
"Text"="@shell32.dll,-30501"
"Type"="radio"
"CheckedValue"=dword:00000002
"ValueName"="Hidden"
"DefaultValue"=dword:00000002
"HKeyRoot"=dword:80000001
"HelpID"="shell.hlp#51104"
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced\Folder\Hidden\SHOWALL]
"RegPath"="Software\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Explorer\\Advanced"
"Text"="@shell32.dll,-30500"
"Type"="radio"
"CheckedValue"=dword:00000001
"ValueName"="Hidden"
"DefaultValue"=dword:00000002
"HKeyRoot"=dword:80000001
"HelpID"="shell.hlp#51105"
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
To remove protectfile.vbs virus from the system
1. Download the free tool MoveOnBoot
2. Open MoveOnBoot
3. Go to Rename Action -> Rename File
4. A dialog box will open, select the file. Since these virus files are hidden files , you won’t be able to browse and see it. Please enter enter “C:\protectfile.vbs” in select-file section.
5. Enter “C:\protectfile.html” in the destination file section. Enter OK.
6. Similarly repeat steps 2 to 4 for the file “C:\autorun.inf” and rename it to “C:\autorun.html”
7. Don’t restart your computer. We have set moveonboot to rename the ProtectFile.vbs in just one of the drives.
8. Repeat step 2 to 5 for each of the drives. For example if you have 4 drives in your computer(C, D, E, F), then you will have to rename “C:\protectfile.vbs”, “D:\protectfile.vbs”, “E:\protectfile.vbs” and “F:\protectfile.vbs” to “C:\protectfile.html”, “D:\protectfile.html”, “E:\protectfile.html” and “F:\protectfile.html” respectively. Similarly rename “autorun.inf” files in all the drives to corresponding “autorun.html” files.
9. Restart your computer. We have disabled the virus.
10. Now we will remove them completely.
11. Open MoveOnBoot again.
12. Go to Delete Actions -> Delete Files
13. You won’t be able to browse and reach the files. So click browse and enter “C:\protectfile.html”, “D:\protectfile.html”, “E:\protectfile.html” ,”F:\protectfile.html”, “C:\autorun.html”, “D:\autorun.html”, “E:\autorun.html” and “F:\autorun.html”
14. Restart your computer.
To remove protectfile.vbs from your system
1. Go to Task manager(Press Ctrl+Alt+Del).
2. In the Processes tab , Kill the processes : explorer and wscript.exe(if available)
3. Now go to Applications tab and press new task
4. Enter cmd .Go to the drive c:\
5. Type del /f/q/a protectfile.vbsand del /f/q/a autorun.inf
6. Go to c:\windows\system32and enter del /f/q/a secureguard.vbsNow you have deleted all the infected files in your system
7. Goto regedit(enter regedit in Run) and search for protectfile.vbs and delete all entries with this name.
8. Now search for the secureguard.vbs and modify it as in the path del only"c:\windows\system32\secureguard.vbs... and let the other part of the path be there alive..
9. Restart your system
Configure TCP/IP from the Command Prompt
In order to configure TCP/IP settings such as the IP address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, DNS and WINS addresses and many other options you can use Netsh.exe.
Netsh.exe is a command-line scripting utility that allows you to, either locally or remotely, display or modify the network configuration of a computer that is currently running. Netsh.exe also provides a scripting feature that allows you to run a group of commands in batch mode against a specified computer. Netsh.exe can also save a configuration script in a text file for archival purposes or to help you configure other servers.
Netsh.exe is available on Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003.
You can use the Netsh.exe tool to perform the following tasks:
Configure interfaces
Configure routing protocols
Configure filters
Configure routes
Configure remote access behavior for Windows-based remote access routers that are running the Routing and Remote Access Server (RRAS) Service
Display the configuration of a currently running router on any computer
Use the scripting feature to run a collection of commands in batch mode against a specified router.
What can we do with Netsh.exe?
With Netsh.exe you can easily view your TCP/IP settings. Type the following command in a Command Prompt window (CMD.EXE):
netsh interface ip show config
With Netsh.exe, you can easily configure your computer's IP address and other
TCP/IP related settings. For example:
The following command configures the interface named Local Area Connection with the static IP address 192.168.0.100, the subnet mask of 255.255.255.0, and a default gateway of 192.168.0.1:
netsh interface ip set address name="Local Area Connection" static 192.168.0.100 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.1 1
(The above line is one long line, copy paste it as one line)
Netsh.exe can be also useful in certain scenarios such as when you have a portable computer that needs to be relocated between 2 or more office locations, while still maintaining a specific and static IP address configuration. With Netsh.exe, you can easily save and restore the appropriate network configuration.
First, connect your portable computer to location #1, and then manually configure the required settings (such as the IP address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, DNS and WINS addresses).
Now, you need to export your current IP settings to a text file. Use the following command:
netsh -c interface dump > c:'location1.txt
When you reach location #2, do the same thing, only keep the new settings to a different file:
netsh -c interface dump > c:'location2.txt
You can go on with any other location you may need, but we'll keep it simple and only use 2 examples.
Now, whenever you need to quickly import your IP settings and change them between location #1 and location #2, just enter the following command in a Command Prompt window (CMD.EXE):
netsh -f c:'location1.txt
or
netsh -f c:'location2.txt
and so on.
You can also use the global EXEC switch instead of -F:
netsh exec c:'location2.txt
Netsh.exe can also be used to configure your NIC to automatically obtain an IP address from a DHCP server:
netsh interface ip set address "Local Area Connection" dhcp
Would you like to configure DNS and WINS addresses from the Command Prompt? You can. See this example for DNS:
netsh interface ip set dns "Local Area Connection" static 192.168.0.200
and this one for WINS:
netsh interface ip set wins "Local Area Connection" static 192.168.0.200
Or, if you want, you can configure your NIC to dynamically obtain it's DNS settings:
netsh interface ip set dns "Local Area Connection" dhcp
As you now see, Netsh.exe has many features you might find useful, and that goes beyond saying even without looking into the other valuable options that exist in the command